Improving App Responsiveness - 앱 반응성 높이기
Improving App Responsiveness- Apple Developer Documentation 을 소개합니다 📲
< 📑 목차 >
- Overview
- Detect Unresponsive Scrolling - 응답하지 않는 스크롤 탐지
- Detect App Hangs - 앱 중단 탐지
- Find the Cause of a Hang - Hang(중단)의 원인 찾기
- Remove Hangs from your App - 앱에서 Hang(중단) 제거
- Use Grand Central Dispatch or OperationQueue - GCD 또는 OQ 사용
- Write Performance Tests to Spot Potential Hangs - 잠재적 Hang(중단)을 감지하기 위한 성능 테스트 작성
Improving App Responsiveness
Apple Developer Doumentation 중 앱 반응성을 향상시키는 아티클을 발견했습니다! 평소 관심있던 부분이라서 이 아티클을 번역해봤어요! 앱의 반응성을 향상시키기 위한 내용과 더불어 MetricKit 에 대해서도 소개하고 있습니다! MetricKit 사용법에 대해서는 다음 포스트에서 소개하겠습니다 💃🕺
이 아티클에는 hang이라는 표현이 자주 등장하는데요! 정확히 딱 매칭되서 번역되는게 없는 것 같아서
저는 hang을 늘어지는 것, 어디 걸려있는 것 쯤의 느낌으로 즉각즉각 반응해서 실행되지 않고 홀딩되는 상태로 이해하고 번역했습니다!
Overview
An app that responds instantly to users’ interactions gives an impression of supporting their workflow. When the app responds to gestures and taps in real time, it creates an experience for users that they’re directly manipulating the objects on the screen. An app that doesn’t respond within a short time shatters this illusion, and leaves users wondering whether the app works correctly at all.
The human perception system is adept at identifying motion, and linking cause to effect through sequential actions. It doesn’t take long for a person to observe a gap between two events as a pause. Users can form the impression that an app is inert and unresponsive after a delay as short as a few tenths of a second. Apps therefore have to react to a user’s actions very quickly to maintain the user’s confidence in their behavior.
요약하자면 유저(사람)는 일시정지로 관찰되는 두 이벤트 사이 간 간격을 오래 보지 않고, 1초의 10분의 1정도 짧은 지연시간 후에 응답하지 않는다면 앱이 비활성화 상태이거나 응답하지 않는다는 인상을 형성할 수 있다고 하네요. 그마만큼 앱의 반응성은 유저가 앱을 사용할 때 중요하다는 걸 설명하고 있습니다. 그렇기 때문에 앱은 유저의 신뢰를 유지하기 위해 사용자 행동에 굉장히 빠르게 대응합니다.
Detect Unresponsive Scrolling
응답하지 않는 스크롤 탐지
Scrolling content appears to jump or “hitch” when the updated content isn’t ready for the next screen refresh. View the hitch rate in the Scrolling pane of the Xcode Organizer window or by using MetricKit.
업데이트된 콘텐츠가 다음 화면 새로 고침을 위한 준비가 되지 않았을 때 스크롤 내용이 점프하거나 “hitch”* 하는 것처럼 나타납니다. Xcode Organizer window의 Scrolling pane에서나 Metric Kit를 사용하여 히치 비율를 볼 수 있습니다.
- hitch: (잠깐 지체하게 하는) 문제[장애]

Detect App Hangs
앱 중단 탐지
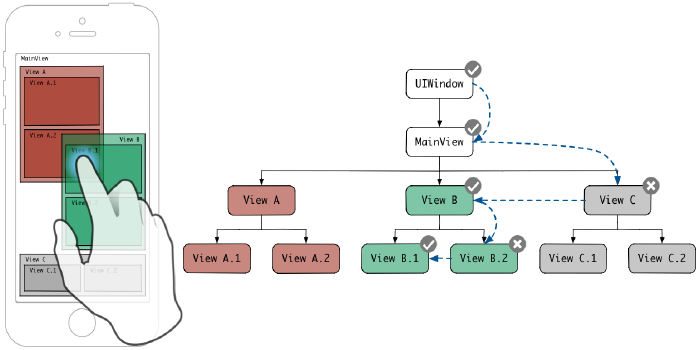
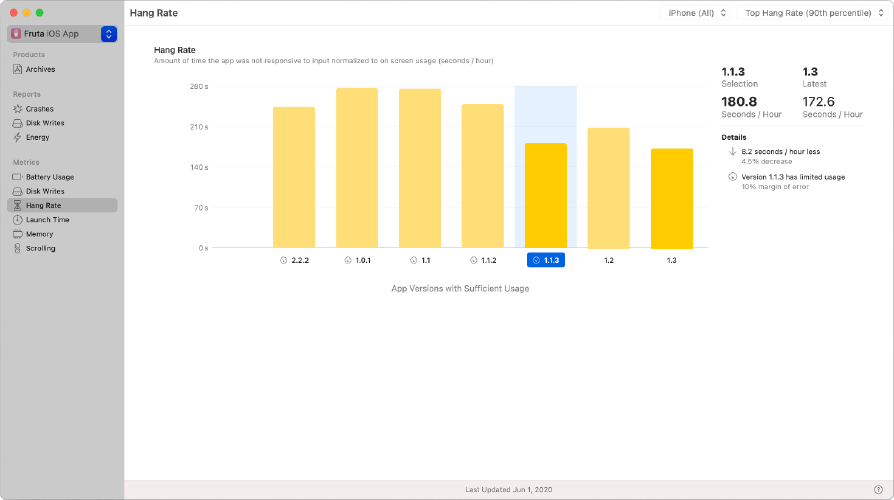
A “hang” is a specific example of an app failing to respond. An app hangs when it isn’t able to update view content or respond to user actions because the main thread is unavailable. iOS detects when apps hang, and makes the data available through MetricKit and Xcode’s metrics organizer. iOS tracks app hangs when the main thread is unresponsive for at least 250ms, and you can see those results in the metrics organizer, as shown below.
“hang”은 앱이 응답하지 않는 구체적인 예입니다. ① main 스레드를 사용할 수 없어 뷰 콘텐츠를 업데이트할 수 없거나(view 업데이트는 main 스레드에서만 가능하기 때문) ② 사용자 작업에 응답할 수 없을 때 앱이 중단됩니다. iOS는 앱이 중단되는 때를 감지하고 MetricKit 및 Xcode의 metrics organizer를 통해 데이터를 사용할 수 있도록 합니다. iOS는 main 스레드가 250ms 이상 응답하지 않을 때 앱의 hangs를 추적하며, 아래와 같이 metrics organizer에서 결과를 확인할 수 있습니다.(아래 그림 참조)

The Xcode Organizer reports the hang rate as the number of seconds per hour that the app is unresponsive. The Organizer shows both the median hang rate experienced by the typical user, and the extreme 90th percentile hang rate. MetricKit provides the same hang rate metric as a histogram.
iOS supports a broad variety of devices with different hardware capabilities and performance characteristics. Code that performs flawlessly on one hardware model could hang on another. Test the release build of your app on a range of different devices to uncover hangs that only manifest in certain circumstances.
Xcode Organizer는 hang rate를 앱이 응답하지 않는 시간(초)으로 보고합니다. Organizer는 일반 사용자가 경험하는 median hang rate와 최대 90번째 백분위수 hang rate를 모두 표시합니다. MetricKit는 막대 그래프과 동일한 hang rate metric을 제공합니다.
iOS는 다양한 하드웨어 기능과 성능 특성을 가진 다양한 기기를 지원합니다. 한 하드웨어 모델에서 완벽하게 수행되는 코드가 다른 모델에 hang on 될 수 있습니다. 다양한 장치에서 앱의 릴리스 빌드를 테스트하여 특정 상황에서만 나타나는 hang(중단 상태, 장애)를 파악합니다.
Find the Cause of a Hang
Hang(중단)의 원인 찾기
Apps hang because the main thread isn’t available when it’s time for the app to draw to the screen. This can happen for two reasons: either the main thread is busy executing code, or it’s blocked waiting for a resource to become available or a system call to complete. Use the Thread State Trace instrument to discover which situation causes hangs in your app.
The Thread State Trace instrument shows a timeline of the thread’s state, along with a narrative that details the system calls entered, how long they took, and when iOS has scheduled the thread to run. Combine this information with the System Call Trace instrument, which gives summary statistics of the number and duration of system calls made by each thread, to see whether system calls are blocking your main thread.
앱이 화면에 그려질 때 main 스레드를 사용할 수 없기 때문에 앱이 중단됩니다. 이는 두 가지 이유로 인해 발생할 수 있습니다. ① main 스레드가 코드를 실행 중이거나, ② 리소스를 사용할 수 있을 때까지 대기하거나 시스템 호출이 완료될 때까지 차단(block)됩니다. Thread State Track(스레드 상태 추적) 계측기를 사용하여 앱에 어떤 상황이 중단되는지 확인합니다.
Thread State Track instrument(스레드 상태 추적기) 는 입력된 시스템 호출, 걸린 시간 및 iOS가 스레드를 실행하도록 예약한 시간을 상세히 설명하는 서술(narrative)과 함께 스레드 상태의 타임라인을 보여줍니다. 이 정보와 Thread State Track instrument와 결합은 각 스레드에서 수행한 시스템 호출 수와 지속 시간에 대한 요약 통계를 보여주는데, 이를 통해 시스템 호출이 main 스레드를 차단하는지 여부를 확인할 수 있습니다.

Click on a particular invocation of a system call in the narrative to view a backtrace of the thread when it made that system call. Use this information to find out which functions or methods on the main thread cause it to hang.
서술(narrative)에서 시스템 호출의 특정 호출(particular invocation)을 클릭하면 스레드가 시스템 호출을 했을 때의 역추적을 볼 수 있습니다. 이 항목에서는 main 스레드의 어떤 함수 또는 메서드가 main 스레드를 멈추게 하는지 알 수 있습니다.
Remove Hangs from your App
앱에서 Hang(중단) 제거
Make sure your app only interacts with UIKit on the main thread. Direct all other operations to a background thread, operation queue, or Grand Central Dispatch queue. Dispatch the work to that queue or thread asynchronously, and have it asynchronously signal the main thread or queue to update the UI when its background work is done. Don’t synchronize the main thread with a background thread, or make the main thread join a background thread. Both of these actions block the main thread until the work in the background has completed, and deny your app the benefit of concurrent operation.
Separate your UI updates into preparing data for display, and updating view objects to display that data when the view is redrawn. Your app can do the preparation in the background, and only needs to use the main thread to update its views. Indicate to the user that this preparation is underway, giving them the opportunity to cancel or perform other tasks as appropriate.
For example, a particular app uses a
UIRefreshControlto allow the user to pull a table view down, to refresh its content from the network. ThevalueChangedevent on theUIRefreshControltriggers an action method on the app’sUIViewControllersubclass. When UIKit invokes this action method, the app makes a request to the server usingURLSessionandNSURLDataTask. On completion of the network task, the app checks whether the download succeeded. If it did, then the app deserializes a JSON object from the downloaded data, updates properties on its model objects based on the fields in the JSON object, then reconfigures its view to reflect the updated model.Of all of these tasks, only the action method invocation from UIKit and the reconfiguration of the app’s views need to use the main thread. The app can dispatch all other tasks asynchronously to the background, as illustrated below.
앱이 main 스레드의 UIKit과만 상호 작용하는지 확인합니다. 다른 모든 작업을 백그라운드 스레드, operation queue, or Grand Central Dispatch queue로 이동합니다. 작업을 해당 queue 또는 thread로 비동기적으로 보내고(dispatch) main 스레드 또는 queue에 비동기로 신호를 보내어 백그라운드 작업이 완료되면 UI를 업데이트하도록 합니다. main 스레드를 백그라운드 스레드와 동기화하거나 main 스레드가 백그라운드 스레드에 join(합쳐지다, 연결하다, 가입하다)하지 않도록 합니다. 이 두 작업 모두 백그라운드의 작업이 완료될 때까지 min 스레드를 차단하고 동시 작업의 이점(benefit of concurrent operation)을 앱에 거부합니다.
UI 업데이트를 분리하여 표시할 데이터를 준비하고 view를 다시 그릴 때 데이터를 표시할 view 객체를 업데이트합니다. 앱은 백그라운드에서 준비할 수 있으며 main 스레드를 사용하여 view를 업데이트하면 됩니다. 사용자에게 이 준비가 진행 중임을 표시하여, 필요에 따라 다른 작업을 취소하거나 수행할 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다.
예를 들어, 특정 앱은 사용자가 table view를 끌어내려 네트워크로부터 콘텐츠를 새로 고치는 것(아래로 끌어 내리는 터치 이벤트를 통한 새로고침)을 허용하기 위해 (‘UIreshControl’)을 사용합니다. UIRefreshControl의 valueChanged 이벤트는 앱의 UI view controller 하위 클래스에 대한 작업 방법을 트리거합니다. UIKit이 이 작업 방식을 호출하면 앱은 URLSession과 NSURLDataTask을 사용하여 서버에 요청을 합니다. 네트워크 작업이 완료되면 앱에서 다운로드 성공 여부를 확인합니다. 이 경우, 앱은 다운로드한 데이터에서 JSON 개체를 역직렬화(deserializes, Decoding을 말합니다)하고 JSON 객체의 필드를 기반으로 모델 개체의 속성을 업데이트한 다음 업데이트된 모델을 반영하도록 view를 재구성합니다.
이러한 모든 작업 중 UIKit에서 호출되는 action method (action 메서드)와 앱의 view 재구성만 main스레드를 사용하면 됩니다. 앱은 아래 그림과 같이 다른 모든 작업을 백그라운드로 비동기식으로 디스패치할 수 있습니다.

Minimize View Update Time
View 업데이트 시간 최소화
To provide smooth animations that look like continual motion, iOS updates the screen at least 60 times per second. When your app is in the foreground, the drawing code on the main thread needs to complete before the next frame is needed, to avoid dropping frames and appearing jerky. Taking an extremely long time to draw a frame hangs the app.
Use standard UIKit views wherever possible to ensure efficient view drawing. Where you need a custom view or control to provide functionality unavailable from standard UIKit components, its
draw(_:)method should only draw into the specified rectangle. Rely on previously prepared data indraw(_:), don’t perform I/O or complex calculations in this method. Draw only into the rectangle passed as an argument todraw(_:)to avoid expensive computations on view components that aren’t drawn to the screen.A view’s
draw(_:)is only invoked to update the view for a frame ifsetNeedsDisplay()was previously called. You should only callsetNeedsDisplay()when the view’s representation needs updating.
연속 움직임과 같은 부드러운 애니메이션을 제공하기 위해 iOS는 초당 최소 60회 이상 화면을 업데이트합니다. 앱이 foreground에 있을 때 프레임이 떨어지고 jerky(덜컥거리는)해 보이지 않도록 다음 프레임이 필요하기 전에 main 스레드의 drawing code를 완료해야 합니다. 프레임을 그리는 데 매우 오랜 시간이 걸리면 앱이 중단됩니다.
가능한 경우 표준 UIKit 뷰를 사용하여 효율적인 view drawing을 보장합니다. 표준 UIKit 구성 요소에서 사용할 수 없는 기능을 제공하기 위해 사용자 정의 보기 또는 컨트롤이 필요한 경우, ‘draw(_:)’ 메서드는 지정된 직사각형에만 그릴 수 있습니다. 이 방법에서 I/O 또는 복잡한 계산을 수행하지 않는 draw(_:)에서 이전에 준비한 데이터에 의존하십시오. 화면에 그려지지 않는 뷰 구성요소의 값비싼 연산 수행을 피하기 위해 draw(_:) 인수로 전달된 직사각형에만 그립니다. (화면에 그려지지 않는 view components를 그리는 연산 비용이 많이 드는 일을 피하기 위해 draw(_:) 인수로 전달된 직사각형에만 그립니다. )
view의 ‘draw(_:)‘는 ‘setNeedsDisplay()’)가 이전에 호출된 경우에만 frame의 view( view for a frame )를 업데이트하기 호출됩니다. view 표현을 업데이트해야 할 경우에만 setNeedsDisplay()를 호출해야 합니다.
Use Grand Central Dispatch or OperationQueue
GCD 또는 OQ 사용
As the number of threads running on the device increases, iOS schedules each thread less often on a CPU core. Any individual thread—including your app’s main thread—runs on a core for less time.
Grand Central Dispatch (GCD)andOperationQueueboth maintain an internal pool of worker threads that’s tuned to the device capacity and load. Use these technologies, instead of creating your own background threads, to ensure balance between scheduling as much work as possible and allowing iOS to run other threads, including the main thread and operating system tasks.
디바이스에서 실행되는 스레드 수가 증가함에 따라 iOS는 CPU 코어에 각 스레드 스케줄을 적게(less) 잡습니다. 앱의 main 스레드를 포함한 모든 개별 스레드는 코어에서 실행되는 시간이 단축됩니다. GCD(Grand Central Dispatch)와 Operation Queue(Operation Queue)는 모두 디바이스 용량과 부하에 맞춰 조정된 worker threads의 내부 풀을 유지하고 있다. 이러한 기술을 사용하면 백그라운드 스레드를 직접 만드는 대신 가능한 한 많은 작업을 스케줄링하고 iOS에서 기본 스레드 및 운영 체제 작업을 포함한 다른 스레드를 실행할 수 있도록 균형을 유지할 수 있습니다.
Write Performance Tests to Spot Potential Hangs
잠재적 Hang(중단)을 감지하기 위한 성능 테스트 작성
For code that must execute on the main thread, create an XCTest performance test to measure the time spent running the code. Execute the relevant code in a
measure(_:)block. You can either accept the average runtime of your code block as the baseline, or edit the baseline and set it to 0.25s (the maximum time iOS allows for main thread execution before recording a hang). The performance test fails if the code requires significantly longer than the baseline time to execute.
main 스레드에서 실행해야 하는 코드의 경우 XCT 테스트 성능 테스트를 생성하여 코드를 실행하는 데 걸린 시간을 측정합니다. measure(_:) 블록에서 관련 코드를 실행합니다. 코드 블록의 평균 런타임을 기준으로 사용하거나 기준선을 편집하여 0.25초(iOS가 main 스레드를 실행하는 데 허용되는 최대 시간)로 설정할 수 있습니다. 코드가 실행되는 데 기준 시간보다 상당히 긴 시간이 필요한 경우 성능 테스트가 실패합니다.
🤓 MetrickKit에 대해 더 알고 싶다면!
👉🏻
Improving Battery Life and Performance
MetricKit Internals. Insights into your iOS app performance.